Project 6: Final Project
Apply your knowledge to build something amazing!
Final Project: Calorie Calculator
ℹ️ Project Overview Difficulty Level: Intermediate
Estimated Time: 3-4 hours
Skills Practiced:
- DOM manipulation with JavaScript
- Form handling and validation
- Mathematical calculations and formulas
- Conditional logic and functions
- Bootstrap components (modals)
- Event listeners and user interaction
Download your material
What you'll do: Open the project and familiarize yourself with the interface
- Open the StackBlitz template: Open in StackBlitz
StackBlitz Project
stackblitz-starters-euwmcdfb - Other alternative: you can download the source code template from Stackblitz Download Project button if you want to use IDE.
⚠️ IMPORTANT: Before You Start
DO NOT DELETE the existing files in the template:
- Package files
- Any other files you didn't create
ONLY EDIT the necessary files.
Project Overview
Let's create a calorie calculator! Do you know how many calories you need everyday? We'll dive into the formula behind calculating calories and see how it works.
This is the flow of the calorie calculator:
-
About you - Input your gender, weight, height and age group.
-
Calculate your BMR - Find out how much calorie you need to just survive (such as for breathing). That is called your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR). The formula will be given below. Basically, it requires your gender, weight, height and age group to calculate BMR.
-
Calculate Daily Recommended Calorie Intake - Find out how many calories you need to maintain your current weight according to your activity levels. The formula is BMR multiplied by Activity Level.
-
Change your weight - According to your Daily Recommended Calorie Intake, find out how many calories you need to eat daily in order to lose or gain 0.5kg of weight per week.
Visual Project Roadmap 🗺️
- Weight Management - Complete this step
- Weight Gain +750 kcal - Complete this step
- User Input - Complete this step
- Calculate BMR - Complete this step
- Calculate Daily Intake - Complete this step
- Weight Loss -500 kcal - Complete this step
- Show/Hide Results - Display the results to the user
Here is how it would look like:

💡 Study Before You Code Take a moment to study the HTML structure and identify:
- Input elements and their IDs
- The modal structure for results
- How Bootstrap classes are used This understanding will make your JavaScript implementation much smoother!
Part 1 Instructions
📍 Milestone One: Setting Up Your Personal Data
Let's start by adding your values in the HTML using specific attributes.
-
Check your gender. Add the
checkedattribute to your gender input radio tag. -
Set your weight - in the weight input, add the
valueattribute equal to your current weight in kg such as 50. -
Set your height - in the height input, add the
valueattribute equal to your current height in cm such as 150. -
Select your age group - add the
selectedattribute to your age group option. -
Select your activity level - add the
selectedattribute to your activity level option.
⚠️ Common Pitfall Make sure you add the attributes to the correct HTML elements!
checkedis for radio buttons and checkboxesvalueis for input fieldsselectedis for option elements inside select dropdowns
BMR Formula Implementation
Let's implement the BMR formula first. The formula for calculating BMR is as shown:
| Gender | Age Group | BMR (kcal) |
|---|---|---|
| Male | Teenager: 10-17 | (69.4 x weight(kg) + 322.2 x height(m) + 2392) / 4.184 |
| Male | Young adult: 18-29 | (64.4 x weight(kg) - 113.0 x height(m) + 3000) / 4.184 |
| Male | Adult: 30-59 | (47.2 x weight(kg) + 66.9 x height(m) + 3769) / 4.184 |
| Male | Elderly: > 60 |
(36.8 x weight(kg) + 4719.5 x height(m) - 4481) / 4.184 |
| Female | Teenager: 10-17 | (30.9 x weight(kg) + 2016.6 x height(m) + 907) / 4.184 |
| Female | Young adult: 18-29 | (55.6 x weight(kg) + 1397.4 x height(m) + 146) / 4.184 |
| Female | Adult: 30-59 | (36.4 x weight(kg) - 104.6 x height(m) + 3619) / 4.184 |
| Female | Elderly: > 60 |
(38.5 x weight(kg) + 2665.2 x height(m) - 1264) / 4.184 |
Reference: http://www.fao.org/3/aa040e/AA040E15.htm - The FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation (1985)
The reason to divide 4.184 is to convert the answer that you get from kilojoules(kJ) to kilocalories(kcal).
⚠️ Height Conversion Alert! The formula uses height in meters, but users input height in centimeters. Don't forget to divide by 100! This is a common mistake that will throw off all your calculations.
Example: 150cm / 100 = 1.5m
💡 Pay Attention to Operators Notice that some formulas use minus (-) while others use plus (+). Double-check your operators against the table above - using the wrong operator is a common source of errors!
DOM Variable Declaration
Declare the necessary variables and select using DOM:
#weight#height#male#female#teenager#youngAdult#adult#elderly
Like this:
javascript
// Get weight input element
var weight = document.querySelector("#weight");
// Get all other elements similarly...
Creating BMR Function
📍 Milestone 2: Building the BMR Calculator
Create a function called bmr() that returns the user's Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR):
-
Inside the function, declare a constant variable called
kJtoKcaland set the value to 4.184 -
Use if...else to determine which formula to use by checking the gender and age group. See the BMR formula above.
-
Use the
returnkeyword to return the BMR results.
csharp
function bmr() {
const kJtoKcal = 4.184;
// Get values from inputs
// Remember: height needs to be converted to meters!
// Check gender and age group
// Apply the correct formula
// Return the result
}
For example, if male is checked and teenager is selected, return the calculated formula for male teenager.
💡 Debugging Strategy Once you've completed the
bmr()function, test it immediately:javascriptconsole.log(bmr()); // Check if the output matches expected values
Here are 2 examples you can check the formula:
- Male teenager at 55kg and 150cm tall is 1599.49 kcal.
- Female teenager at 45kg and 140cm tall is 1223.88 kcal.
Have you checked your formula if they are correct? If yes, then proceed to the next instruction.
Daily Intake Calculation
📍 Milestone 3: Activity Level Calculations
With the BMR value, we can now calculate the Daily Recommended Calorie Intake by multiplying a number according to the user's activity level. Let's have another function for this.
Declare the necessary variables and select using DOM:
#AL1as sedentary#AL2as light#AL3as moderate#AL4as active
Like this:
javascript
// Activity level selections
var sedentary = document.querySelector("#AL1");
var light = document.querySelector("#AL2");
// Continue for moderate and active...
Create a function called dailyIntake() that returns the user's Daily Recommended Calorie Intake:
The formula is BMR multiplied by Activity Level value.
| Activity Level | Multiply Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sedentary | BMR x 1.2 | Little or no exercise |
| Lightly active | BMR x 1.375 | Exercise 1-3 days/week |
| Moderately active | BMR x 1.55 | Exercise 3-5 days/week |
| Very active | BMR x 1.725 | Exercise 6-7 days/week |
scss
function dailyIntake() {
// Get the BMR value first
var bmrValue = bmr();
// Check which activity level is selected
// Multiply BMR by the appropriate factor
// Return the result
}
💡 Best Practice Use descriptive variable names and add comments to explain what each multiplier represents. This makes your code more maintainable!
Displaying Results
Now that we have the function for dailyIntake(), let's show it in the results!
When we click on the "GET RESULT" button, we will see the Bootstrap modal appear. A modal is a dialog box/popup window that is displayed on top of the current page.
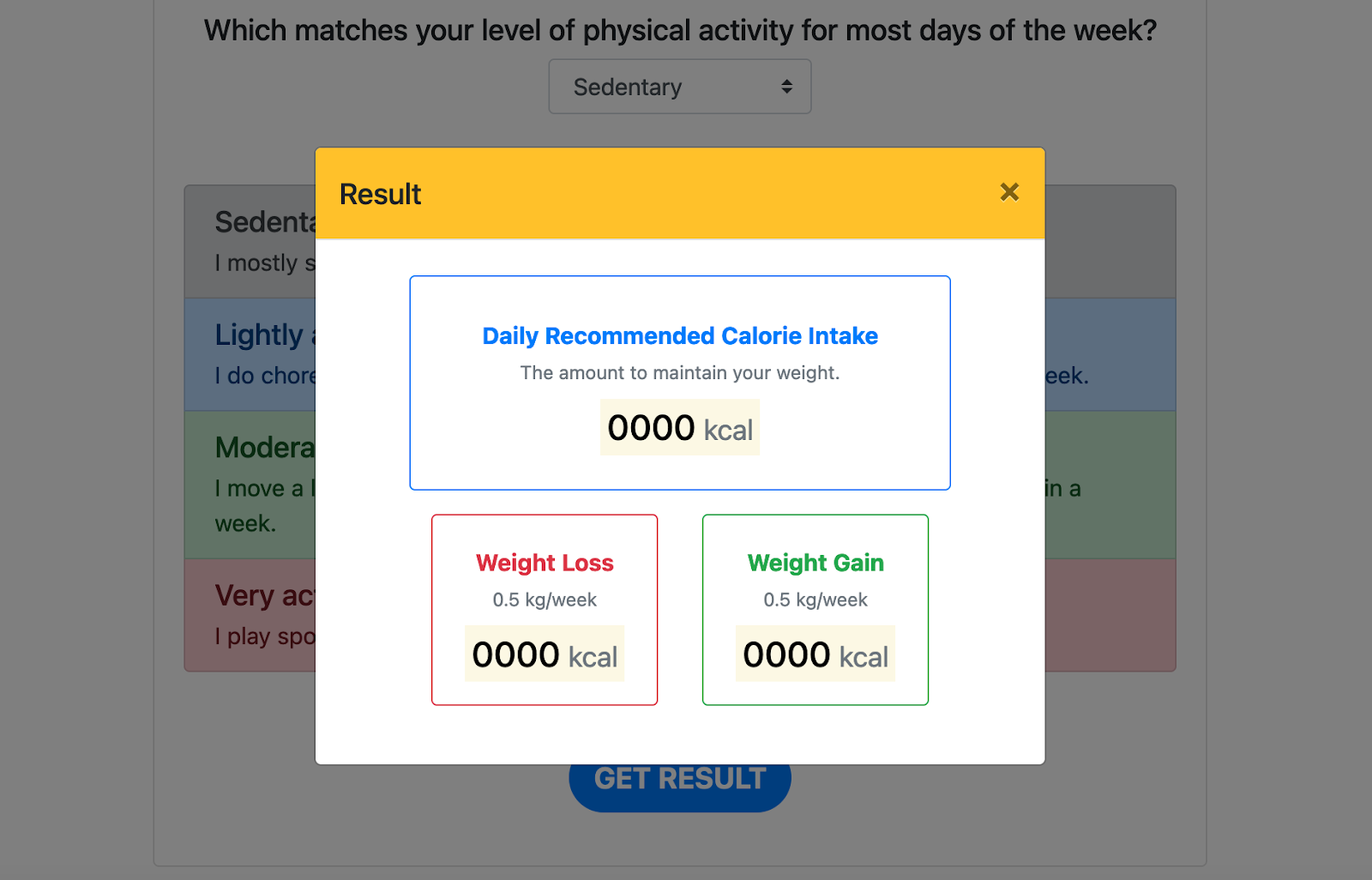
Later in part 2, we will work on the weight loss and weight gain results. For now, you can ignore it first. Let's show the results for the Daily Recommended Calorie Intake.
Declare the necessary variables and select using DOM:
#resultBtn#daily
Like this:
ini
// Button and result display elements
var resultBtn = document.querySelector("#resultBtn");
var daily = document.querySelector("#daily");
Add a "click" event listener to resultBtn:
javascript
resultBtn.addEventListener("click", () => {
// Calculate and display the daily intake
daily.textContent = Math.round(dailyIntake());
});
⚠️ Don't Forget Math.round() Always round your calorie calculations! Nobody needs to know they should eat 2,147.836 calories - 2,148 is much clearer.
Part 2 Instructions
Finally, we will calculate the weight gain and weight loss results.
📍 Milestone 4: Weight Management Calculations
Weight Gain Calculation
For the weight gain result, it is to calculate how many calories you need to eat daily to gain 0.5kg per week. The formula is adding 750kcal to your Daily Recommended Calorie Intake.
The result is your daily recommended calories for weight gain.
Create a function called weightGainCal():
javascript
function weightGainCal() {
// Add 750 calories for healthy weight gain (0.5kg/week)
return Math.round(dailyIntake() + 750);
}
💡 Understanding the Math Why 750 calories? To gain 0.5kg (1.1 lbs) per week, you need a surplus of about 3,500 calories per week. That's 500 calories per day, but we use 750 to ensure healthy muscle gain along with fat.
Weight Loss Calculation
As for the weight loss result, it is to calculate how many calories you need to eat daily to lose 0.5kg per week. The formula is deducting 500kcal to your Daily Recommended Calorie Intake.
The result is your daily recommended calories for weight loss.
Create a function called weightLossCal():
javascript
function weightLossCal() {
// Subtract 500 calories for healthy weight loss (0.5kg/week)
return Math.round(dailyIntake() - 500);
}
Displaying Weight Results
📍 Milestone 5: Safety Checks and Final Display
With both the functions for weight gain and weight loss ready, we can now show these results in our modal.
Declare the necessary variables and select using DOM:
#weightLossCard#weightLoss#weightGain
Weight gain - inside the arrow function for the resultBtn click event, add another line to set the .textContent of weightGain to weightGainCal().
Weight loss - Before we can show the weight loss result, we have to check if the daily recommended calories for weight loss is safe or not. This is because if your calorie intake is already very low and if you reduce the calorie even further to lose weight, it will be unhealthy and can be life-threatening. Not eating enough calories means your body cannot grow or repair properly.
⚠️ Safety First! Never recommend a calorie intake below the minimum safe levels. This is not just about weight loss - it's about health and safety. Your calculator should protect users from dangerous recommendations.
Here is the formula for the minimum daily recommended calories:
- 1600 calories/day for male (All age groups)
- 1200 calories/day for women (18 and above)
- 1400 calories/day for teenage girls (10-17)
Safety Examples
For example:
- Teenage boys must not lose weight if daily recommended calories for weight loss is below 1600kcal.
- Women must not lose weight if daily recommended calories for weight loss is below 1200kcal.
In the index.html file, add a class called d-none to the #weightLossCard tag. This will set its CSS display to none, which hides the weight loss result from showing by default.
Inside the arrow function for the resultBtn click event, use if...else and else if to determine if we want to show weight loss results or not by checking the weightLossCal() value, gender and age group. See the minimum daily recommended calories formula above.
To hide the weight loss results, we just have to replace the class d-block to d-none by using the following code:
arduino
// Hide the weight loss card when it's unsafe
weightLossCard.classList.replace("d-block", "d-none");
To show the weight loss results, we just have to do the opposite by replacing d-none to d-block with the following code:
scss
// Show the weight loss card when it's safe
weightLossCard.classList.replace("d-none", "d-block");
// Don't forget to also update the text content!
weightLoss.textContent = weightLossCal();
💡 Bootstrap Display Classes
d-none= display: none (hidden)
d-block= display: block (visible)
These Bootstrap classes make it easy to show/hide elements without writing custom CSS!
Extension Challenges
Ready to take your calculator to the next level? Try these advanced features!
Challenge One: Data Validation
Let's add data validation. Such as when the weight or height is empty or below a certain value, show [Please enter a valid number] danger text below the input box.

The danger text should appear individually below weight input and height input as shown above:
php-template
<p><small class="text-danger">[Please enter a valid number]</small></p>
By using the same method to toggle show or hide the weight loss result, we can also do the same for the danger text.
Give each of these paragraph <p> tags the d-none class and a unique ID like #weightDanger and #heightDanger.
Add a "keyup" event listener to both the weight and height input. So that when the user finishes typing, it will show the danger text if the input is invalid.
javascript
weight.addEventListener("keyup", () => {
// Check if weight is valid (not empty, above 35kg)
if (weight.value === "" || parseFloat(weight.value) < 35) {
// Show danger text
// Disable button
} else {
// Hide danger text
// Enable button if both inputs are valid
}
});
💡 Validation Thresholds
- Minimum weight: 35kg (to prevent unrealistic values)
- Minimum height: 100cm (to prevent unrealistic values)
- Maximum reasonable values could also be added!
You can also disable the "GET RESULT" button by setting .disabled to true:
ini
resultBtn.disabled = true; // Disabled (Button cannot click)
resultBtn.disabled = false; // Enabled (Button can click)
Challenge 2: Additional Features
Consider adding these enhancements:
- Save calculation history
- Add imperial units option (lbs/inches)
- Create a meal plan suggestion based on calorie needs
- Add a progress tracker for weight goals
Debugging Tips
Having trouble? Here are common issues and solutions:
BMR Calculation Issues
- Wrong values? Check if you're converting height to meters (divide by 100)
- NaN results? Ensure all inputs have values before calculating
- Incorrect formula? Double-check plus/minus operators for each age/gender combo
Display Problems
- Modal not showing? Check if Bootstrap is properly loaded
- Results not updating? Verify event listeners are attached correctly
- Weight loss card always hidden? Check your safety condition logic
Quick Debug Code
arduino
// Add this to debug your calculations
console.log("BMR:", bmr());
console.log("Daily Intake:", dailyIntake());
console.log("Weight Loss Cal:", weightLossCal());
console.log("Is weight loss safe?", weightLossCal() >= minimumSafeCalories);
Project Submission
🎉 Congratulations on completing the Calorie Calculator! This project has taught you valuable skills in DOM manipulation, mathematical calculations, and user safety considerations.
Before You Submit, Check:
- ✅ All formulas calculate correctly
- ✅ Safety checks prevent dangerous recommendations
- ✅ The modal displays all results properly
- ✅ (Optional) Validation prevents invalid inputs
When you have completed your "Calorie Calculator" project, submit it using the link below:
💡 Final Check Test with different combinations of gender, age, weight, height, and activity levels to ensure your calculator works for all users!