Concept 17: Object Detection with YOLO Algorithm
Object Detection with YOLO Algorithm
:dart: Learning Objectives
By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
- Understand what object detection is and how it works
- Explain the YOLO algorithm and its advantages
- Compare YOLO with Haar Cascades
- Implement object detection using YOLOv8 in Python
- Apply object detection to both images and videos
What is Object Detection?
:information_source: Object Detection is a computer vision technique that helps computers identify and locate objects within images or videos. It's like teaching a computer to "see" and recognize things the way humans do!
Object detection helps us:
- Find different types of objects in pictures (like people, cars, or animals)
- Show exactly where these objects are located
- Draw boxes around objects with labels to identify them

:rocket: You Only Look Once (YOLO)
:information_source: YOLO (You Only Look Once) is a super-fast object detection algorithm that can find and identify multiple objects in images or videos in real-time. It looks at the entire image just once to detect all objects!
How YOLO Works
YOLO was created in 2015 by researchers Joseph Redmon, Santosh Divvala, Ross Girshick and Ali Farhadi. Here's what makes it special:
- Like playing "I Spy": YOLO looks at a picture and quickly finds all the objects in it
- Super fast: It only needs to look at the image once (that's where the name comes from!)
- Smart detection: It can find many objects at the same time

:bulb: Remember: YOLO gets its name because it only needs to look once at an image to find all the objects. This makes it much faster than older methods that had to scan the image multiple times!
:emoji: Comparing Haar Cascades and YOLO
Haar Cascades
Haar Cascades work by:
- Using many simple patterns called Haar features
- Scanning the image step by step
- Looking for specific features in each area
YOLO Approach
YOLO is different because it:
- Looks at the entire image at once
- Uses deep learning to understand the whole picture
- Finds all objects in one quick scan
Quick Comparison
Features Haar Cascades YOLO Speed Slower ⏱️ Fast :zap: Accuracy Good for simple objects Better, especially for complex scenes Computer Power Needed Less demanding :computer: Needs more power :emoji:️ :books: YOLO Version History
YOLO has improved over the years! Here are the different versions:
- YOLOv1 (2015) - The original version
- YOLOv2/9000 (2016) - Faster and more accurate
- YOLOv3 (2018) - Better at detecting small objects
- YOLOv4 (2020) - Even more improvements
- YOLOv5, YOLOv6, YOLOv7 (2022) - Multiple versions with different strengths
- YOLOv8 (2023) - The newest and best version! note We'll use YOLOv8 in this lesson because it's:
- The newest version (2023)
- More accurate than older versions
- Easier to use with helpful features
:emoji: Real-World Applications
YOLO helps us in many ways:
Medical Field :emoji:
- Finding organs in medical scans - Doctors use YOLO to spot kidneys and other organs in CT scans
 (Image from Kidney Recognition in CT using YOLOv3)
(Image from Kidney Recognition in CT using YOLOv3)
Agriculture :emoji:
- Detecting ripe fruits - Farmers use YOLO to find tomatoes ready for picking
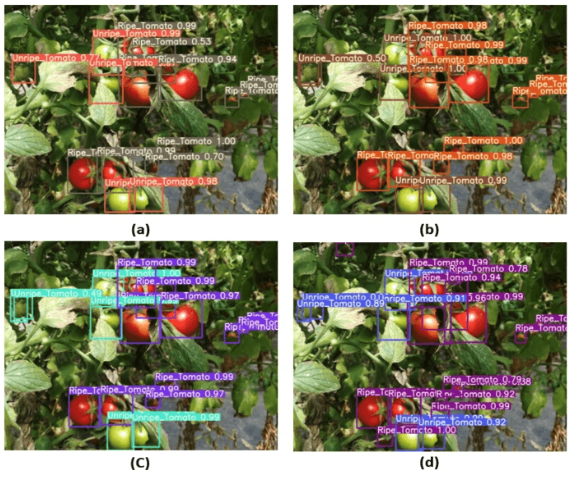
Transportation :emoji:
- Self-driving cars - YOLO helps cars "see" pedestrians, other vehicles, and traffic signs

:bulb: Want to learn more? Check out this article by Datacamp for extra details!
:computer: Let's Code with YOLOv8!
We'll build our object detection program in three easy steps:
- Install the tools - Get YOLOv8 and OpenCV ready
- Load a trained model - Use a pre-trained YOLO model
- Detect objects - Find objects in images and videos
Step One: Install and Import Ultralytics :package:
First, we need to install the Ultralytics package that contains YOLOv8. Choose the right command for your computer:
- For Windows users:
bashpip install ultralyticsOr
bashpy -m pip install ultralytics
- For Mac users:
bashpython3 -m pip install ultralyticsnote Having trouble? Download the requirements.txt file, put it in your project folder, and run:
- For Windows users:
bash
py -m pip install -r requirements.txt
- For Mac users:
bash
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
- For Google Colab users, run the following code in your colab file to install Ultralytics.
bash
!pip install ultralytics

After installation is complete, import the libraries we need:
python
from ultralytics import YOLO
import cv2 as cv
Step 2: Load a Trained Model :emoji:
Now we'll load a pre-trained YOLO model. Think of this like downloading a brain that already knows how to recognize objects!
python
# Load trained model
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
Next, let's get the list of objects this model can recognize:
python
# Load the labels
class_names = model.names
Step 3: Detect Objects in Images :emoji:️
Let's use our YOLO model to find objects in an image! First, we load the image:
python
img = cv.imread("image.jpg")
Then, we ask YOLO to find objects in the image:
python
# Detect objects
results = model.predict(source=img)
Now comes the fun part - drawing boxes around the objects YOLO found:
python
# Draw bounding boxes
for result in results:
boxes = result.boxes
for box in boxes:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box.xyxy[0]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2)
cv.rectangle(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# Put classname with confidence
text = class_names[math.floor(box.cls)] + " " + str(math.floor(box.conf * 100)) + "%"
cv.putText(img, text, (x1, y1), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
Finally, let's show the image with all the detected objects:
python
# Display the resulting frame
cv.imshow('Image', img)
Keep the window open until a key is pressed:
python
# Keep image window open until user presses a key
cv.waitKey(0)
Complete Code for Image Detection
Here's the complete program that detects objects in an image:
python
from ultralytics import YOLO
import cv2 as cv
import math
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
class_names = model.names
img = cv.imread("image.jpg")
results = model.predict(source=img)
# Draw bounding boxes
for result in results:
boxes = result.boxes
for box in boxes:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box.xyxy[0]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2)
cv.rectangle(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# Put classname with confidence
text = class_names[math.floor(box.cls)] + " " + str(math.floor(box.conf * 100)) + "%"
cv.putText(img, text, (x1, y1), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# Display the resulting frame
cv.imshow('Image', img)
cv.waitKey(0)
:movie_camera: Detecting Objects in Videos
We can also detect objects in videos! YOLO will analyze each frame of the video. First, let's load a video:
python
# Capture video
video = cv.VideoCapture("video.mp4")
# Capture webcam image
video = cv.VideoCapture(0)
Now we'll process the video frame by frame:
python
while True:
# Capture frame-by-frame
ret, frame = video.read()
# Quit when no more frame
if not ret:
print("Video Ended")
break
# Run object detector
results = model.predict(source=frame)
# Draw bounding boxes
for result in results:
boxes = result.boxes
for box in boxes:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box.xyxy[0]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2)
cv.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# Put classname with confidence
text = class_names[math.floor(box.cls)] + " " + str(math.floor(box.conf * 100)) + "%"
cv.putText(frame, text, (x1, y1), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# Display the resulting frame
cv.imshow('frame', frame)
# stop when Q is pressed
if cv.waitKey(25) == ord("q"):
break
Don't forget to clean up when done:
python
# When everything done, release the capture
video.release()
cv.destroyAllWindows()
:emoji: Summary
In this lesson, you learned:
- Object detection finds and identifies objects in images
- YOLO is a fast algorithm that looks at images just once
- YOLOv8 is the newest and most accurate version
- How to implement object detection in Python for both images and videos
YOLO has many real-world uses, from helping doctors analyze medical scans to enabling self-driving cars to "see" the road!
Video Tutorial
:emoji: Practice with AI
Ready to explore more? Try these AI prompts to deepen your understanding:
Learning Prompts:
- "What are the advantages of using YOLOv8 for object detection?"
- "Explain how YOLO differs from traditional object detection methods"
- "What types of objects can YOLOv8 detect?"
Coding Prompts:
- "Write Python code to implement object detection with YOLOv8"
- "How can I detect only specific objects (like cars) using YOLO?"
- "Create a program that counts the number of people in an image using YOLO"
Project Ideas:
- "Help me build a pet detector using YOLOv8"
- "How can I use YOLO to create a traffic monitoring system?"
- "Guide me in making a fruit counting app with YOLO"


