Concept 18: Deep Learning & Image Classification
Deep Learning & Image Classification
:dart: Learning Objectives
By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
- Understand what deep learning is and how it mimics the human brain
- Identify different deep learning frameworks and their uses
- Distinguish between AI, machine learning, and deep learning
- Explain the image classification process and its applications
- Compare image classification with object detection
:emoji: What is Deep Learning?
:information_source: Definition: Deep Learning is a subfield of machine learning that mimics how the human brain works. It uses layers of artificial neurons to process information, just like our brain cells communicate with each other.
Deep learning is like the smart student who learned from machine learning! While machine learning needs guidance, deep learning can figure things out on its own by looking at lots of examples.

How Does Deep Learning Work?
Deep learning copies how your brain works by using:
- Data inputs (like your eyes seeing things)
- Weights (how important each piece of information is)
- Biases (your brain's preferences)
These parts work together to help computers recognize and understand things, just like you do!
:rocket: Real-World Applications
Deep learning powers amazing technologies:
- Self-driving cars - Cars that can see and understand the road
- Customer service chatbots - Virtual assistants that can help you
- Photo colorization - Adding color to old black-and-white photos
- Language recognition - Understanding what you say
- Translations - Converting text between languages
- Computer vision - Helping computers "see" like humans
Types of Deep Learning Algorithms
:memo: Deep learning algorithms are like different tools in a toolbox. Each one is good at solving different problems!
Supervised Deep Learning (learns with a teacher):
- Artificial Neural Network (ANN) - Basic brain-like networks
- Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) - Great for understanding images
Unsupervised Deep Learning (learns on its own):
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) - Creates new images or data
- Self Organizing Map (SOM) - Organizes information into groups
:hammer_and_wrench: Deep Learning Frameworks
:information_source: Deep Learning Frameworks are like ready-made toolkits that help you build AI models quickly. Instead of building everything from scratch, you can use these tools to create amazing AI projects!
Think of frameworks as LEGO sets for AI - they give you pre-built pieces that you can combine to create something awesome!
Popular Python Frameworks
TensorFlow - Google's powerful AI toolkit with ready-to-use models
Keras - Works with TensorFlow to make AI even easier to use
PyTorch - Facebook's flexible framework loved by researchers
:emoji: Understanding AI, ML, and DL
tip Think of these as nested boxes: AI is the biggest box, ML fits inside AI, and DL fits inside ML!
Artificial Intelligence (AI) :emoji:
AI makes machines smart like humans. It's the big idea of giving computers human-like abilities.
Machine Learning (ML) :books:
ML teaches computers to learn from examples:
- Computers learn patterns from data
- They make predictions based on what they learned
- Watch this video about ML to learn more!
Deep Learning (DL) :emoji:
DL is ML's super-smart cousin:
- Copies how our brain works
- Finds complex patterns automatically
- Watch this video about DL to see it in action!
:bar_chart: Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
| Aspect | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Features | You tell it what to look for | Figures out what to look for |
| Amount of data | Needs lots of examples | Needs TONS of examples |
| Hardware requirements | Regular computer | Powerful computer |
| Training time | Quick to train | Takes longer to train |
| Testing time | Slower to use | Super fast to use |
| Example usage | Netflix recommendations | Self-driving cars |
Learn more about these differences in this helpful article.
:emoji:️ Image Classification
:information_source: Image Classification is teaching computers to recognize what's in a picture and put it in the right category - just like sorting your photos into folders!
Image classification helps computers understand pictures like you do!
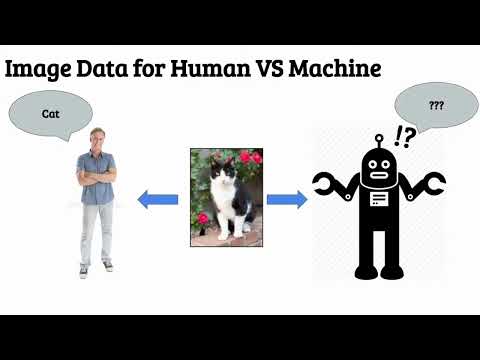
Example: Teaching Computers to See
Look at this picture:

You instantly know it's a cat, right? But computers need to learn this skill through deep learning!
:star2: Where We Use Image Classification
- Social Media - Tags your friends in photos automatically
- Online Shopping - Find products by taking a picture
- Photo Apps - Organizes your photos by what's in them
- Self-Driving Cars - Recognizes stop signs, pedestrians, and other cars
:clipboard: The Image Classification Process

:memo: Building an image classifier is like teaching a student - you need examples, practice, and tests!
Step One: Prepare Dataset :emoji:
Collect lots of example images:
- Gather images for each category
- Convert images to numbers (computers only understand numbers!)
- Use existing datasets from libraries like TensorFlow or websites like Kaggle
Step 2: Data Preprocessing :wrench:
Get the data ready:
- Transform images into computer-friendly format
- Resize all images to the same size
- Adjust brightness and colors if needed
Step 3: Build the Model :emoji:️
Create your AI brain:
- Choose a deep learning algorithm
- Design the network structure
- Different setups give different results!
Step 4: Train the Model :emoji:
Teach your model:
- Show it thousands of examples
- Let it learn patterns
- Practice makes perfect - train multiple times!
Step 5: Test and Evaluate :white_check_mark:
Check how well it learned:
- Use new images it hasn't seen
- Measure accuracy
- Make improvements if needed
:mag: Image Classification vs Object Detection
tip Quick Comparison:
- Image Classification = "What's in this picture?"
- Object Detection = "What's in this picture and where is it?"
Both help computers understand images, but:
- Image Classification tells you what the main subject is
- Object Detection finds multiple objects and shows exactly where they are

:memo: Summary
In this lesson, you learned:
- Deep Learning mimics the human brain to solve complex problems
- Frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch make building AI easier
- Image Classification teaches computers to recognize what's in pictures
- The process involves preparing data, building models, training, and testing
- Deep Learning is more powerful than regular Machine Learning but needs more data
:emoji: Learn More
:emoji: Practice with AI
Try these prompts to explore deep learning further:
Understanding Concepts:
- "What are the key differences between machine learning and deep learning?"
- "Explain how image classification works in simple terms"
Hands-on Coding:
- "Write Python code to build a simple image classification model"
- "Show me how to load and preprocess images for deep learning"
Real-world Applications:
- "Give me 5 creative uses of image classification in everyday life"
- "How do self-driving cars use deep learning to see the road?"