Concept 9: Document Object Model
Document Object Model (DOM)
Definition: HTML DOM stands for Document Object Model which allows JavaScript to modify all the elements of an HTML document.
DOM is a programming interface for HTML:
- All the HTML properties, attributes, methods, events can be changed with DOM.
- This includes changing the CSS and its classes.
Basically HTML DOM is how we can get, change, add, or delete HTML elements.
DOM Tree Structure
Just like how we have learnt to write HTML, there is a hierarchical structure and that looks like branches of a tree.
Install this Google Chrome extension to see the DOM tree structure: https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/html-tree-generator/dlbbmhhaadfnbbdnjalilhdakfmiffeg/related


Here is an example code: https://glitch.com/edit/#!/wise-foamy-jester

We will be using this example code below for our notes examples:
html
<body>
<div class="text-center">
<h1 class="display-3">HTML DOM</h1>
<p class="text-primary">
A programming interface for HTML.
</p>
<img
class="w-50"
src="https://cdn.glitch.com/..."
alt="DOM logo"
/>
<p id="love" class="text-danger">
I love JavaScript [heart]
</p>
</div>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</body>
When you show the website using the extension, the DOM tree structure of the index.html looks like this:

All HTML elements now in the DOM are called nodes.
It always starts with the HTML document, then the body, and then whatever node the website has such as <div>, <h1>, <p>, <img>, etc.
Selecting DOM Elements
Let's learn how to select the nodes in DOM using some common DOM methods.
There are 2 common ways to select an element and store its reference in a variable:
| DOM Methods | Explanation |
|---|---|
document.querySelector() |
Select the first element that appears in the HTML document. |
document.querySelectorAll() |
Select all elements and return as an array-like object called a NodeList |
CSS Selectors
These DOM methods require a selector in the parenthesis. The selector is based on the CSS selector:
"p"(Get the paragraph tag element) - Just write the tag name."#love"(Get the element using an id called "love") - Write the # symbol before the id name.".text-primary"(Get the element that has a class name called "text-primary") - Write the full stop (.) symbol before the class name.
You can learn more of these CSS selectors here: https://www.w3schools.com/cssref/css_selectors.asp
querySelector() Example
Based on the HTML code above, here is an example of using the querySelector() method and selecting using id:
javascript
var textLove = document.querySelector("#love");
console.log(textLove);
Browser console (F12):

querySelectorAll() Example
Based on the HTML code above, here is an example of using the querySelectorAll() method by selecting the tag:
javascript
var allParagraphs = document.querySelectorAll("p");
console.log(allParagraphs);
Browser console (F12):

Because in the HTML example above, there are 2 <p> tags and so here, the 2 <p> tags are selected in an array called a NodeList.
Modifying Elements
Now that we know how to select a node using the 2 common DOM methods, let's try modifying the node with CSS styles.
Adding CSS Styles
Here is an example of adding a CSS style to an element:
javascript
var header = document.querySelector("h1");
header.style.backgroundColor = "yellow";

As you can see the .style.backgroundColor is the same as the CSS background-color.
You can find a list of all the CSS style names for DOM here: https://www.w3schools.com/jsref/dom_obj_style.asp
Working with Classes
Since Bootstrap uses the class attribute to change the appearance, let's try modifying the node's class attribute using the classList property.
Adding Classes
Here is an example of adding a class to an element:
javascript
var header = document.querySelector("h1");
header.classList.add("bg-primary", "text-white");

Removing Classes
Here is an example of removing a class of an element:
javascript
var p1 = document.querySelector(".text-primary");
p1.classList.remove("text-primary");

Creating and Removing Elements
Adding a Node
To add a node using DOM basically means adding an HTML element to your page.
There are a few steps to creating a node:
- Select where you want the new HTML element to be placed inside.
- Create the HTML element you want to add and give it some text or attributes.
- Use the
.appendChild()method to add the new HTML element to an existing HTML element.
For this example, we will be using the same HTML code from DOM (Part 1): https://glitch.com/edit/#!/wise-foamy-jester

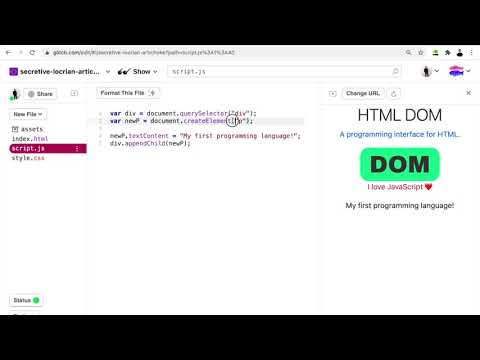
Let's add a paragraph element inside the div:
javascript
var div = document.querySelector("div");
var newP = document.createElement("p");
newP.textContent = "My first programming language!";
div.appendChild(newP);

Removing a Node
To remove a node basically means to remove an HTML element.
The steps are simple for removing a node:
- Select the HTML element you want to remove.
- Use the
.remove()method to remove the HTML element.
In this example, using the same example HTML as before, we remove the image:
javascript
var image = document.querySelector("img");
image.remove();

Additional DOM Methods
There are actually around 90 different DOM methods you can use in JavaScript. You can check this link for the list: https://www.w3schools.com/jsref/dom_obj_all.asp
Summary
| Operation | Method/Property | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Select Element | querySelector() |
document.querySelector("h1") |
| Select Multiple | querySelectorAll() |
document.querySelectorAll("p") |
| Change Style | .style |
element.style.color = "red" |
| Add Class | .classList.add() |
element.classList.add("active") |
| Remove Class | .classList.remove() |
element.classList.remove("hidden") |
| Create Element | createElement() |
document.createElement("div") |
| Add to DOM | .appendChild() |
parent.appendChild(newElement) |
| Remove Element | .remove() |
element.remove() |
The DOM is the bridge between HTML and JavaScript, allowing you to create dynamic and interactive web pages.
Key Concepts Summary
- The DOM represents HTML documents as a tree structure of nodes that JavaScript can manipulate
- querySelector() selects the first matching element, while querySelectorAll() selects all matching elements
- CSS selectors are used to target elements by tag name, class (.className), or ID (#idName)
- Element styles can be modified using the .style property with camelCase CSS property names
- Classes can be added or removed using classList.add() and classList.remove() methods
- New elements are created with createElement() and added to the DOM with appendChild()
- Elements can be removed from the DOM using the .remove() method
- The DOM provides the bridge between HTML structure and JavaScript functionality